The world of manufacturing has evolved tremendously over the years. The increasing demand for high-quality and intricate products requires a level of precision and efficiency that traditional manufacturing methods struggle to achieve.
When it comes to turning your idea into a product, precision is the key to success. One way you can achieve it is to fabricate your parts with state-of-the-art manufacturing processes like computer numerical control (CNC) precision machining.
This article explains CNC precision machining and answers some of the most frequently asked questions about it.
What is CNC Precision Machining?
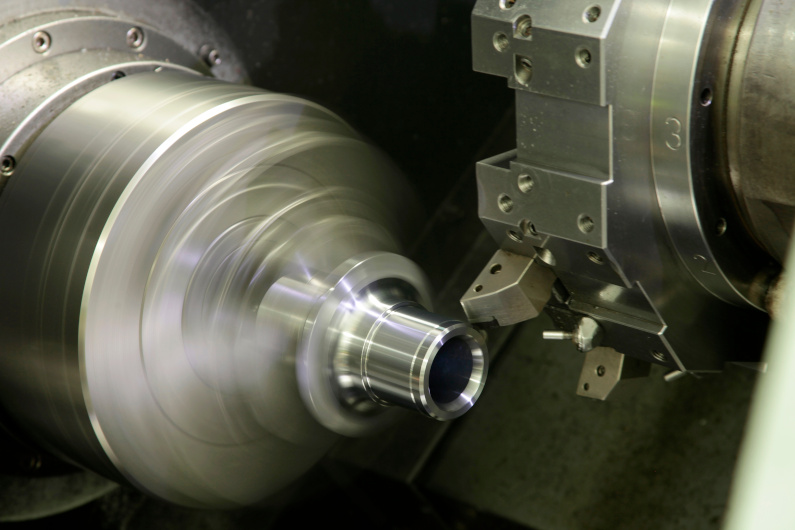
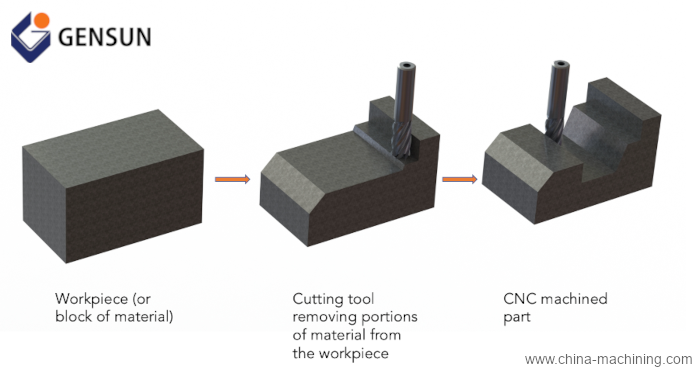
CNC precision machining is a subtractive manufacturing process─which means it involves removing portions of material from a workpiece till the desired product is formed.
This process is quite similar to conventional milling and lathe operations. However, with precision machining, computer numerical control technology controls the sequence of movement of the workpiece and cutting tools to fabricate the parts accurately and precisely.
Before making any product by CNC machining, you need to first create the 3D computer-aided design (CAD) of your desired part using CAD or CAM programs. Next, your machinist converts this CAD file into G-code─which is a computer program the CNC machine uses to automate the manufacturing process.
Learn More: What is CNC Machining?
Question #1 What is the Achievable Engineering Tolerance of CNC Precision Machining?
Without a doubt, CNC machines offer higher accuracy and precision than other manufacturing technologies. However, CNC machines cannot reproduce the dimensions of your part just as they are in the CAD blueprint.
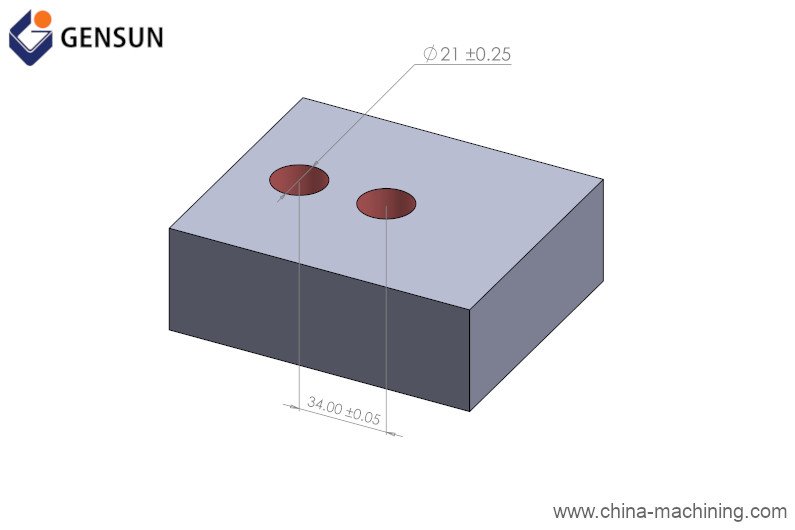
That is to say; there will always be some deviation in the dimension of your machined part. Product designers and machinists use engineering tolerance to specify the acceptable amount of deviation in the dimension of a part.
For instance, say you’re looking to manufacture a shaft with a nominal diameter of 20 mm. If the functionality of your shaft isn’t affected by a deviation of up to 0.01 mm, then you can specify your engineering tolerance as ±0.01 mm (pronounced plus or minus 0.01 millimeters).
So if your machine shop ends up manufacturing a shaft with a diameter of 20.01 mm or 19.99 mm, you’d still expect your part to be functional.
Learn More: Machining Tolerances 101
Question #2 What are the Most Common Types of CNC Precision Machining Equipment?
In product development, machinists often use several types of CNC machining equipment to fabricate your product. The choice of CNC machining equipment primarily depends on your product design features and complexity. For instance, here is a list of the most common types of CNC machines and their applications:
CNC Milling Machines
These machines feature a multi-bladed cutting tool that rotates against a stationary workpiece. This CNC machining equipment is ideal for creating cavities, angled cuts, and off-center holes.
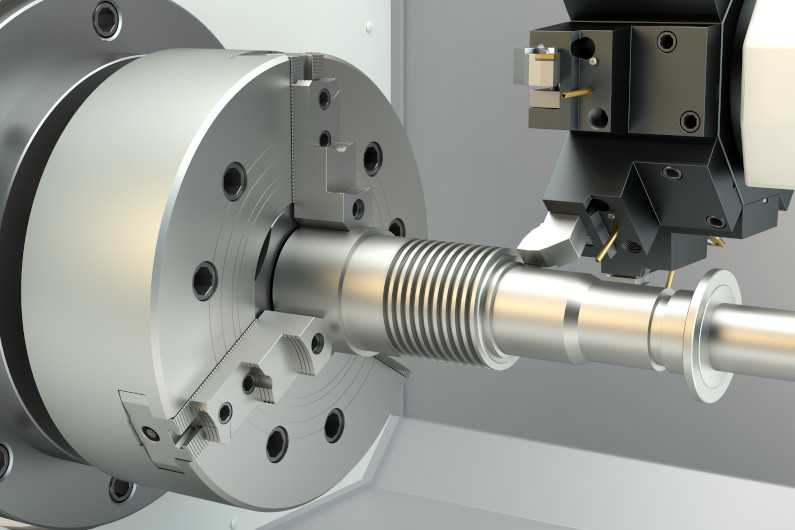
CNC Turning Machines
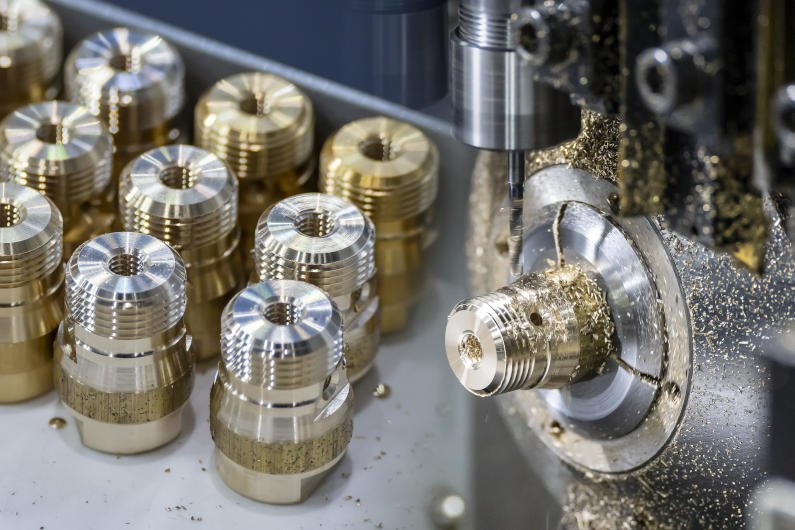
In these machines, the workpiece is attached to a chuck and made to rotate against a stationary cutting tool. CNC turning machines are ideal for fabricating complex cylindrical shapes. You can also use them for reaming, thread cutting, spot facing, and knurling operations.
CNC Electrical Discharge Machine
These are quite similar to CNC lathes and milling machines─they use CNC technology to automate the manufacturing process. However, unlike CNC lathes and milling machines that use machining tools to create cuts, an electrical discharge machine uses electrical sparks to cut the workpiece. These machines are ideal for creating micro slots, angled features, and holes in difficult-to-machine metals.
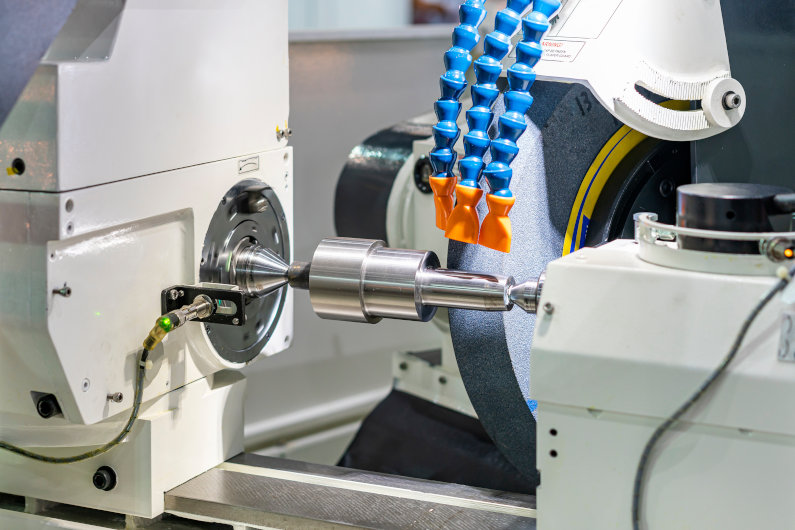
CNC Grinding Machines
These machines use abrasive wheels to remove material from a workpiece, achieving tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes. CNC grinding machines are commonly used to produce precision components for industries such as aerospace and automotive.
Learn more: 10 Types of CNC Machines and Their Applications
Question #3 What are the Top Applications of CNC Precision Machining?
CNC precision machining has made it possible to produce a wide range of high-quality products across various industries. The high precision of CNC machining equipment makes them ideal in several industries, including the automotive, aerospace, and medical industries. Some examples include:
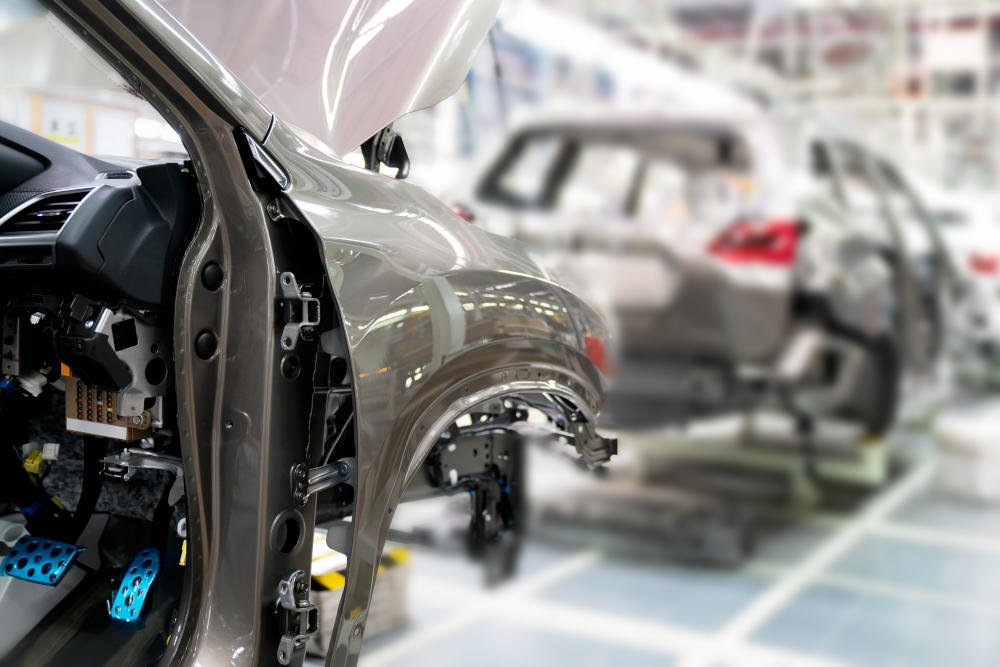
Automotive Industry
CNC precision machining allows auto parts manufacturers to meet the stringent requirements of today’s automotive industry. For instance, modern gearboxes and engine blocks are quite small and require tight tolerances to be functional. CNC machines are being used to manufacture these essential parts precisely. In addition, CNC machines are helping to machine lightweight alloys used in vehicles’ interior and roof panels.
Learn more: Applications of CNC Machining in the Automotive Industry
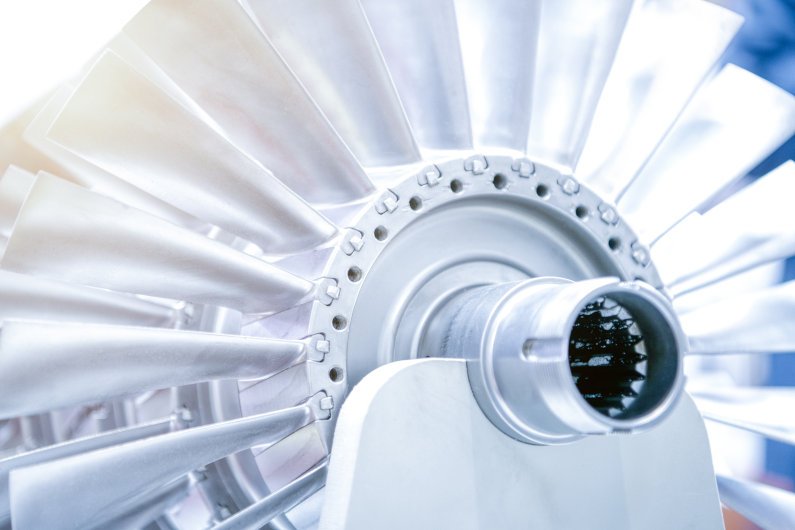
Aerospace Industry
Nothing is as important as precision in aerospace parts manufacturing. And as you may have guessed, CNC machines allow manufacturers to fabricate complex aircraft parts accurately. For instance, aircraft manufacturers rely on CNC machines to fabricate aircraft fuselage sections and landing gears.
Learn more: Applications of CNC Machining in the Aerospace Industry
Medical Industry
CNC machines are at the forefront of technologies used in the medical industry. For instance, applications of CNC machines in this industry include the fabrication of medical implants and surgical instruments (like blades and scissors).
Learn more: Applications of CNC Machines in the Medical Industry
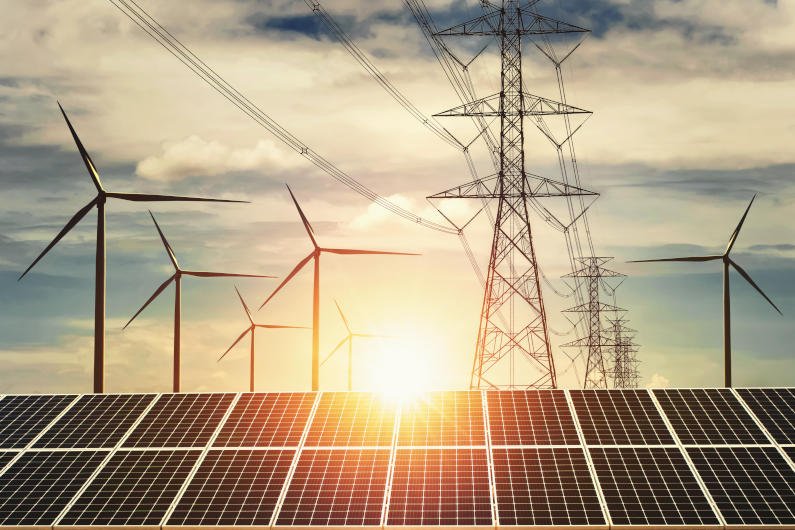
Energy Industry
In the renewable energy sector, precision machining is employed to manufacture components for wind turbines, solar panels, and fuel cells. These parts must be highly accurate and reliable to ensure the efficient operation of renewable energy systems.
Learn more: CNC Machining for the Energy Industry
Electronics Industry
Precision machining is essential for producing electronic components, such as circuit boards and connectors, with tight tolerances and intricate features. This technology enables the production of increasingly small and complex devices, driving innovation in the electronics industry.
Learn more: CNC Machining for the Electronics Industry
Question #4: What are the Advantages of Precision Machining?
Precision machining boasts a plethora of advantages that make it a top choice for manufacturers, revolutionizing the way products are created across various industries. Here are some of the most compelling benefits of this cutting-edge technology:
Unparalleled Accuracy and Precision
CNC machines achieve jaw-dropping tolerances as minute as ±0.004 mm, guaranteeing that the end product is flawlessly aligned with design specifications and performs impeccably as intended.
Astounding Flexibility
Precision machining effortlessly crafts an incredible array of parts with diverse complexities, making it indispensable across numerous industries and applications. This adaptability empowers manufacturers to swiftly respond to shifting market demands and evolving product designs.
Lightning-fast Speed and Efficiency
Automated CNC machines operate tirelessly around the clock, slashing production times and supercharging manufacturing efficiency. This results in accelerated lead times, allowing products to reach the market at breakneck speeds.
Unwavering Consistency
Precision machining delivers unwavering quality across multiple production runs, eradicating the need for manual adjustments and minimizing the risk of human error. This consistency ensures reliable performance and drastically reduces the chances of product defects or recalls.
Material Versatility
Precision machining excels in working with a vast assortment of materials, from metals and plastics to composites, offering unparalleled flexibility in product design and development. This versatility enables manufacturers to handpick the most suitable materials for specific applications, optimizing product performance and resilience.
Minimal Waste
Precision machining techniques expertly eliminate material waste by surgically removing only the required material from the workpiece. This efficient use of materials translates to significant cost savings and a lighter environmental footprint.
Impressive Scalability
Precision machining is adept at handling both low-volume and high-volume production runs, allowing manufacturers to effortlessly scale their operations in response to market demand. This scalability ensures optimal resource utilization and enables production adjustments to meet ever-changing customer needs.
Seamless Integration with Advanced Technologies
Precision machining can be harmoniously integrated with other groundbreaking manufacturing technologies, such as additive manufacturing and robotics, to further amplify production capabilities. This seamless integration paves the way for innovative manufacturing solutions that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and elevate product quality.
Boundless Customization
Precision machining enables the creation of tailor-made parts for specific applications, facilitating exceptional product differentiation and the development of specialized solutions. This level of customization offers a formidable competitive edge for manufacturers, enabling them to cater to the unique needs and demands of their customers.
CNC Precision Machining: Gensun Can Help
CNC machining is ideal for fabricating high-quality parts while satisfying tight tolerance requirements. However, the success of your manufacturing project also depends on the CNC machining shop you work with.
Gensun Precision Machining is a leading provider of CNC machining services across Asia. We’ve been in business for nearly two decades, providing high-quality machining services for customers across various industries.
Learn more about our CNC machining services.